Sign In
The Rotation of Two Dimensional Geometric Objects







| | 13 Theory slides |
| | 8 Exercises - Grade E - A |
| | Each lesson is meant to take 1-2 classroom sessions |
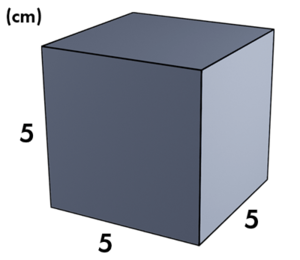
Cross-Sections of a Cube
In the diagram, a cube is given. Try to identify how many different cross-sections can be formed. What geometric shapes do these cross-sections have?

Rotating a Circle

Extra
How to Use the AppletThese are the possible interactions with the presented applet.
- To rotate the circle, click on the button
Rotate
or click on the circle and move it around. - To see the formed three-dimensional figure from different perspectives, click on its interior region and drag it.
- To return to initial image, click on the button
Reset.
Cross-Sections of a Sphere

Extra
How to Use the AppletThese are possible interactions with the presented applet.
Rotating a Rectangle

Extra
How to Use the AppletThese are the possible interactions with the presented applet.
- To choose the side to be the axis of rotation, click on the longer or shorter side.
- To rotate the rectangle, click on the
Rotate
button. - To look at the formed three-dimensional figure from different perspectives, click on its interior region and drag it.
- To return to initial image, click on the
Reset
button.
Cross-Sections of a Right Cylinder
From the previous applet, it could be concluded that rotating a rectangle about one of its sides forms a right cylinder. What are the cross-sections of a right cylinder? There are several types depending on the position of an intersecting plane.
| Case | Position of the Plane | Cross-Section |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Perpendicular to the base | Rectangle |
| 2 | Parallel to the base | Circle |
| 3 | Diagonal to the base | Ellipse |
The following applet illustrates each type of the mentioned cross-sections.

Pairing a Plane with a Cylinder's Cross-Section

Hint
Analyze the shapes of the cross-sections closely. What conclusions can be drawn about the sides and angles of the cross-sections?
Solution
To pair each plane with the corresponding type of cross-section, each given case should be investigated.
Plane A
The first intersecting plane is parallel to the cylinder's bases. Therefore, the cross-section it creates has the same shape as the bases, which are circles.

Hence, the cross-section is also a circle.
Plane B
The intersecting plane is perpendicular to both bases of the cylinder. Since the cylinder is right, the cross-section has four right angles. Additionally, the longer sides of the cross-section are parallel to the height of the cylinder and have the same lengths.

Furthermore, the shorter sides are parallel chords of the cylinder's bases, which also have equal lengths. Therefore, the cross-section is a rectangle.
Plane C
The last plane intersects only the curved surface of the cylinder, so it does not have straight sides. The cross-section has a circular shape, but it is not a circle.

Recall the possible cross-sections of a right cylinder depending on the position of the intersecting plane.
| The Plane's Position | Cross-Section |
|---|---|
| Perpendicular to the base | Rectangle |
| Parallel to the base | Circle |
| Diagonal to the base | Ellipse |
Since the intersecting plane is diagonal to the bases of the cylinder, it can be concluded that the cross-section is an ellipse.
Identifying the Types of a Cylinder's Cross-Sections
The given two-dimensional shape is a cross-section of a right cylinder. Identify whether the cross-section is parallel, perpendicular, or diagonal to the base of the cylinder.

Rotating a Right Triangle

Extra
How to Use the AppletThese are the possible interactions with the presented applet.
- To choose the axis of rotation of a triangle, click on either of its two legs (each of them can be treated as the height of the triangle).
- To rotate the triangle, click on the button
Rotate.
- To see the formed three-dimensional figure from different perspectives, click on its interior region and drag it.
- To return to the initial image, click on the button
Reset.
Cross-Sections of a Cone
From the previous applet, it can be observed that when rotating a right triangle about its height, a right cone is formed. What are the cross-sections of a right cone? Here are some possible types depending on the position of an intersecting plane.
| The Plane's Position | Cross-Section |
|---|---|
| Perpendicular to the base | Triangle |
| Parallel to the base | Circle |
| Diagonal to the base | Ellipse |

Pairing a Plane with a Cone's Cross-Section

Hint
Analyze the shapes of the cross-sections closely. What conclusions can be drawn about the sides and angles of the cross-sections?
Solution
To pair each plane with the corresponding type of cross-section, each given case should be analyzed.
Plane A
The first intersecting plane is parallel to the cone's base. Consequently, the cross-section it creates has the same shape as the base, which is a circle.

Therefore, the cross-section is also a circle.
Plane B
The second plane goes through the curved surface of the cone, so it does not have any straight sides. The cross-section has a circular shape, but it is not a circle.

To identify the cross-section, the possible cross-sections of a right cone can be reviewed.
| The Plane's Position | Cross-Section |
|---|---|
| Perpendicular to the base | Triangle |
| Parallel to the base | Circle |
| Diagonal to the base | Ellipse |
It can be noticed that the intersecting plane is diagonal to the bases of the cone. Therefore, the cross-section can be concluded to be an ellipse.
Plane C
The last intersecting plane is perpendicular to the base of the cone and goes through the vertex of the cone. The cross-section has three vertices, which are connected by sides.

Therefore, the cross-section is a triangle.
Identifying Cross-Sections of a Cone
The given 2D shape is a cross-section of a right cone. Identify whether the cross-section is parallel, perpendicular, or diagonal to the base of the cone.

Other Possible Cross-Sections of a Cone

| 3D Object | Intersecting Plane's Position | Cross-Section |
|---|---|---|
| Sphere | Any position | Circle |
| Right Cylinder | Perpendicular to the base | Rectangle |
| Parallel to the base | Circle | |
| Diagonal to the base | Ellipse | |
| Right Cone | Perpendicular to the base | Triangle |
| Parallel to the base | Circle | |
| Diagonal to the base | Ellipse |

The region enclosed by the semicircle is revolved completely about the horizontal axis.

Determine the following measures for the solid of revolution in terms of π.
When we revolve the semicircle about the x-axis, we get a sphere. Since the radius of the semicircle is 4 centimeters, we also get a sphere with a radius of 4 centimeters.
Let's use the formula for the volume of a sphere to calculate its volume.
The volume is 2563π cubic units.
Using the formula for the surface area of a sphere, we can calculate the surface area of the sphere.
The surface area is 64π square units.
To determine which of the solids are the result of a revolution about an axis, let's first discuss the characteristics of such a solid.
Solid of Revolution
When a two-dimensional object is rotated around an axis, the resulting solid of revolution will have rotational symmetry along this axis. Additionally, the edges of the shape that is rotated will necessarily form a circle. Below we see an example of this by rotating a rectangle around the y-axis, forming a cylinder.
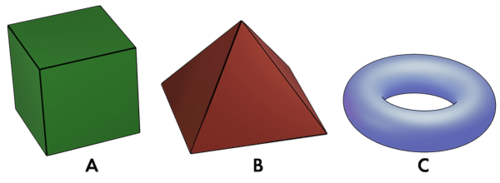
The Cube and the Pyramid
If we look at the cube and the pyramid, we see that both the cube and the pyramid have 90^(∘) rotational symmetry about a vertical axis through the center of their respective bases.
However, since the edges of the solids are not circular, neither of them can be the result of revolving it around an axis.
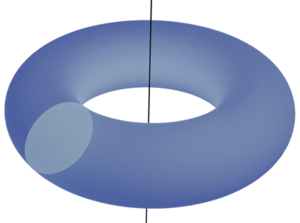
The Torus
As for the doughnut-looking solid, also known as a torus, we see that it has rotational symmetry around a vertical axis through its center, and its outer edges have the shape of a circle.
Therefore, the torus can be created by revolving a circle about an axis.
For each solid, what is the area of the cross-section fitting the following description? Give the answer in exact form.
The cross-section runs parallel to the base.
The cross-section runs perpendicular to the base and goes through the center of the base.
The cross-section runs parallel to the base.
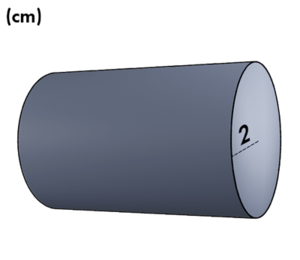
A cross-section of a solid is the two-dimensional shape created when a plane intersects the solid at a certain point and angle. In this case, the plane cuts the cylinder at an angle parallel to its base. This means the resulting shape is a circle.
Since the cylinder has a radius of 2 centimeters, we can determine the area of the cross-section by using the formula for the area of a circle.
The area is 4π square centimeters.
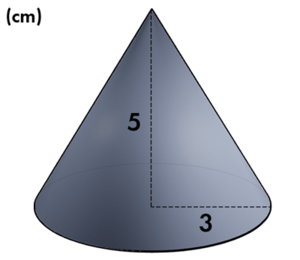
Let's start by drawing the cross-section. We know that it should run perpendicular to the base and it should also go through the cone's center. In this case, the shape created is an isosceles triangle.
We know that the cone has a radius and a height of 3 and 5 centimeters, respectively. This means the base of the cross-section is 2*3 =6 centimeters. With this information, we can calculate the area of the triangle.
The area is 15 square centimeters.
Let's draw the cross-section of the cube. We know that the plane is parallel to the square base. Therefore, the cross-section must also be a square.
The cube has a side of 5 centimeters. From here, we can use the formula for the area of a square to calculate the area.
The area is 25 square centimeters.
What is the volume of the solid created by rotating the polygon about the given axis? Give the answer in terms of π.



By rotating a rectangle around an axis, we get a solid of revolution that is a cylinder. Since the rectangle is a square with a side of 10 centimeters, the resulting cylinder has a radius and height of both 10 centimeters.
Now we can calculate the volume of the cylinder.
The volume of the cylinder is 1000π cubic centimeters.
When we rotate a right triangle about an axis, we get a solid of revolution that is a cone.
As we can see, the cone has a height and a radius of 9 centimeters. With this information, we can figure out the volume of the cone.
The volume of the cone is 243π cubic centimeters.
As in the first section, we get a cylinder when revolving a rectangle around an axis.
Let's calculate the cylinder's volume.
The volume of the cylinder is 20π cubic centimeters.